rockwell hardness test used for|disadvantages of rockwell hardness test : wholesaling The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different . See more Resultado da A Federação Paulista de Futebol (FPF) realizou, nesta quarta-feira, o sorteio dos grupos da próxima edição da Copa São Paulo de Futebol Júnior, a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webSweet exchange (Princess Connect! Re:Dive) [Otochichi] Subscription Mama! (COMIC Mugen Tensei 2024-01) [Chinese] [皇色汉化] nhentai is a free hentai manga and .
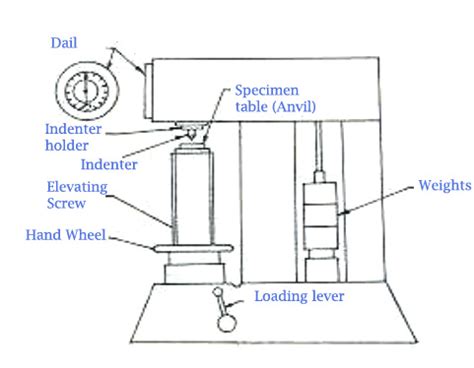
The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different . See moreThe differential depth hardness measurement was conceived in 1908 by Viennese professor Paul Ludwik in his book Die Kegelprobe (crudely, "the cone test"). The differential-depth method . See moreThe Rockwell hardness test can be conducted on several various hardness testers. All testers, however, fall under one of three categories. Bench model hardness testers can be found . See more
There are several alternative scales, the most commonly used being the "B" and "C" scales. Both express hardness as an arbitrary See more• International (ISO)• US standard (ASTM International) See more• Brinell hardness test• Hardness comparison• Holger F. Struer• Knoop hardness test See more
• Video on the Rockwell hardness test• Hardness Conversion Chart• Rockwell to brinell conversion chart• Hardness Conversion Table See moreRockwell hardness test measures the permanent depth of indentation on the material by applying a fixed load using an indenter. The smaller the .
The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method. You should obtain a copy of this standard, read and understand the standard completely before attempting a Rockwell test. Hardness testing is commonly used for material evaluation due to its simplicity and low cost, relative to other assessments of these qualities. .In hardness testing according to Rockwell, the total test force is applied in two steps. This is intended to eliminate effects from the roughness of the specimen surface (e.g., grooves on the specimen) as well as measurement errors .
rockwell hardness tester diagram
The Rockwell hardness test at a glance: Generally used for larger samples. No optical readout. Can be used for advanced tests. Standards: ASTM E18, ISO 6508 and JIS Z 2245. See our complete range of Rockwell hardness testing . The Rockwell hardness test is the industry standard measuring system used to determine how resistant a material is to another object. Hardness is defined as a material’s resistance to permanent indentation.The Rockwell test consists of measuring the additional depth to which a carbide ball or Brale® diamond penetrator is forced by a heavy (major) load beyond the depth of a previously applied . In the Rockwell hardness test, the measure of the hardness is not an indentation surface but an indentation depth. Either a carbide ball or a rounded diamond cone with a tip angle of 120° and a tip radius of 0.2 mm .
Two broad types of tests are used: the Rockwell superficial hardness and the Rockwell regular hardness tests. Brinell: A spherical indenter is used, and the diameter of the resulting indentation is measured to give the .The Rockwell hardness test is widely used in various industrial applications, such as manufacturing, engineering, and quality . The Brinell hardness testing method is used in various cases where large or rough surfaces, coarse-grained materials, or high loads are involved. It is particularly well-suited for testing the hardness of
Hardness test methods in the macro range include Brinell, Vickers and Rockwell. Hardness testing in the low-load range applies when the test load falls between an interval of 0.2 kgf and 5 kgf (test load ≥ 0.2 kgf and < 5 kgf). The most commonly used low-load method is Vickers. Low-load hardness testing is mainly used for testing of small .
Conducting a hardness test using the Rockwell hardness method can be difficult, especially if you misunderstand its principles and application. Not to overstate it, but without an understanding of the Rockwell hardness method, you might end up going round in circles or, worse still, end up with an inaccurate material hardness value.To accommodate the hardness testing of this diverse range, several different indenter types are used in the Rockwell hardness testing along with a range of standard force levels. Each combination of indenter type and applied force levels has been defined using a distinct Rockwell hardness scale. As per ASTM E 18, there are thirty (30) different . The equation for the Rockwell hardness test for metals is below: d=depth from zero load point. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. Rockwell A scale. Used to test: Tungsten carbide. Rockwell B Scale. Used to test: aluminum, brass, and softer steels. Rockwell C Scale. Used to test: harder steels.
Basic principle and practical procedure of the Rockwell hardness test - Testing machine, test piece, conical diamond indenter - Basic principle, hardness d.A widely used variant of the Rockwell hardness test is the superficial Rockwell test, wherein the minor load is 3 N and the major loads are 15, 30, or 45 N.Further details on the Rockwell superficial hardness scales are available in the relevant ASTM standards (ASTM 1984).The Rockwell hardness values are expressed as a combination of hardness number and a scale .
The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method. The Rockwell test is generally easier to perform and more accurate than other hardness methods. The Rockwell test method is used on all metals except in circumstances where the test metal structure or surface condition would introduce too .In the Rockwell hardness testing, the indenter applies the first load to the test piece. The indent is then measured, and the value obtained is used for the base calculations. This first load is removed, and another heavier load is applied to the indenter on the test piece. The Rockwell hardness of the test piece is calculated by subtracting .
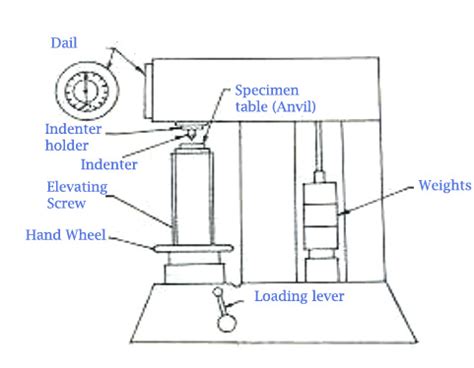
rockwell hardness test diagram
Foremost to any Rockwell test process is identification of the proper hardness scale to be used on the component to be tested. There are 30 different Rockwell scales with the majority of applications covered by the Rockwell HRC and HRB scales for testing most steels, brass, and other metals.The Rockwell hardness test is widely used to standardize the hardness of metals. Although it is possible and easy to perform, it can be time-consuming and expensive. It is also important to note that since the hardness of a material is determined by the Rockwell Hardness number, it doesn’t indicate whether the material with that number will . Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via a diamond in this method. The Rockwell hardness test, according to ASTM E18-24, is an indentation hardness test that involves the use of a verified machine to force a diamond spheroconical indenter or tungsten carbide (or steel) ball indenter .
How Many Tests Are There for the Rockwell Regular Test Scales? The Rockwell Hardness Tester has many different scales depending on the application of the tester on different materials. There is a total of 30 . Every Rockwell hardness scale is identified by a letter signifying the indenter type and the two loads used for the test. A Rockwell hardness number is a combination of the numerical hardness value and the letter for .The Rockwell Hardness Test is one of several tests used to determine whether a material is solid and durable enough to be employed as a component of an object. The Knoop, Brinell, and Vickers procedures are additional examinations in the sequence. Process The Rockwell Hardness test and its counterparts [.]
The Rockwell hardness test continues to be applied as a tool for assessing the properites of a product while the tolerances on the acceptable material hardness have become tighter and tighter. Adhering to good practice procedures when performing Rockwell hardness measurements and calibrations is a beneficial step to reducing measurement errors. Figure 1. An operator performing a Rockwell hardness test. (Source: Arkansas Department of Transportation.) The Rockwell hardness is calculated using the following formula: Rockwell Hardness, HRC = [0.2 – permanent depth of indentation (mm)] x 500. The Rockwell hardness test was developed to be less destructive and cheaper than the Brinell test.Load: The Rockwell hardness test uses a pre-load of 10 kgf, followed by the application of the main load, which varies depending on the Rockwell scale being used (e.g., 60 kgf for the Rockwell A scale, 150 kgf for the Rockwell C scale). The load is applied for a .The Rockwell hardness test method is a simple process that uses a diamond cone with a round tip for harder materials and a hardened steel ball indenter for softer ones. With every test, two loads are applied to the test subject. First, an indenter is forced into the test subject under an initial load of 10kg-f, and the depth is recorded.
The Rockwell hardness test has a variety of applications. It is not only used to determine material properties according to hardness and forming processes, but also for quick and effective testing in production and incoming goods departments. This helps ensure that the material meets specified requirements and will behave optimally when used .Scale C (carbide) testers are used for testing cemented carbides in the Rockwell A Scale, where tolerances of ± 0.20 of a Rockwell Hardness point are required. A specially selected “A” Brale penetrator is used to measure the hardness of cemented carbides in accordance with ASTM B 294 and the Cemented Carbide Producer’s Association (CCPA).
There are two types of Rockwell test (Table 23.1): Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. Table 23.1: Some common scales in Rockwell and Superficial Rockwell testing
However, the Rockwell hardness test does not serve well as a predictor of other properties such as strength or resistance to scratches, abrasion, or wear, and should not be used alone for product design specifications. Different Rockwell hardness scales utilize different size steel balls and different loads. The three most common scales used .A widely used variant of the Rockwell hardness test is the superficial Rockwell test, wherein the minor load is 3 N and the major loads are 15, 30, or 45 N. Further details on the Rockwell superficial hardness scales are available in the relevant ASTM standards (ASTM 1984).The Rockwell hardness values are expressed as a combination of hardness number and a scale .
bond seal strength tester
box hill high school seal test
9 de ago. de 2023 · Notas de Corte da Residência Médica ENARE: Unirio, UFF, UFMG, HF Lagoa, HF Ipanema, HCPM RJ, e HF Bonsucesso. Caros leitores do nosso blog médico, .
rockwell hardness test used for|disadvantages of rockwell hardness test